How can I tell if a citation generated by AI is real?
Answer
AI tools such as ChatGPT can often generate citations to resources that don't exist, known as AI hallucinations.
It is therefore important to know how to spot fake or hallucinated citations and to understand how to locate the source so you can verify the information within it.
Determine the type of source: book, book chapter, journal article, thesis, conference paper, etc.
- Journal articles will include an issue and volume number, a journal and an article name.
- Books will include a publisher's name, like Taylor and Francis, Oxford University Press, etc.
- Conference papers will include the name of the conference or the conference proceedings. e.g. "Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multiagent Systems, AAMAS"
- Theses include descriptions such as Master's Thesis.
What to look for when checking citations:
- Citations that are incomplete or missing important information that helps identify the source, such as the author, article, and journal title.
- Links that don't work or that open an incorrect article or page.
- Inconsistent referencing format, i.e. citations that differ vastly from the referencing styles you may be familiar with (e.g., APA7).
One or a combination of these may indicate that your citation may be a hallucination. Use the guidance below to verify your resource.
Strategies to try to verify your resource:
- Use the following tools to locate the details of the resource. You may need to check more than one.
- Use different searches, including combinations to search for the:
- Journal Title
- Article Title
- Author
- Full citation in quotation marks if using Google Scholar
- Navigate to Google Scholar.
- Copy and paste your citation (enclosed in quotation marks "") and select search.
"Qinran, Y., & Weiqun, C. (2021). Video‐Driven 2D Character Animation. Chinese Journal of Electronics, 30(6), 1038–1048. https://doi.org/10.1049/cje.2021.07.016"
- Check all details are correct and the resource exists.
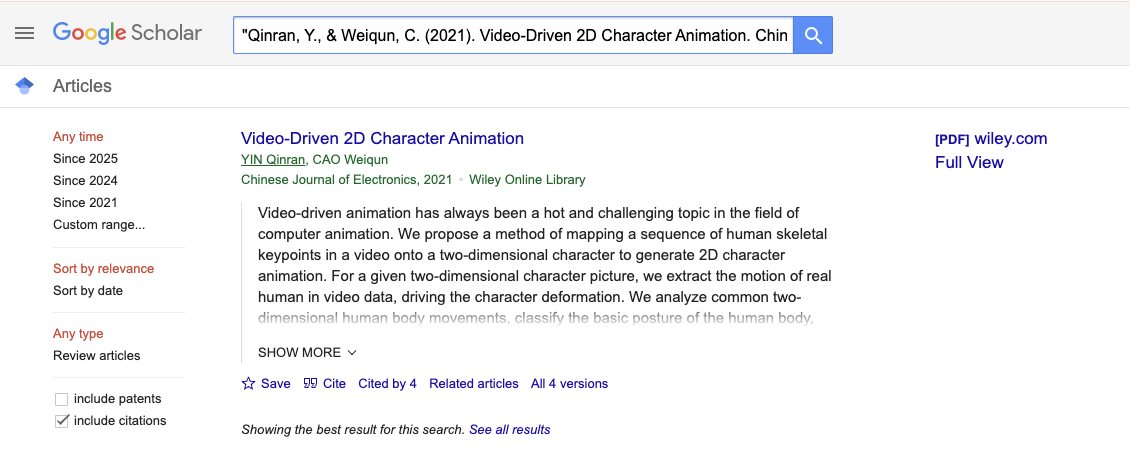
- When you locate the resource (or details of the resource), match all the following details against the AI citation:
- Author
- Date
- Article Name
- Volume and Issue Number
- Journal Name
Additional Tips:
- Don't ask large Language Models like ChatGPT to generate a list of references. Chat GPT scans the internet for resources but does not have the ability to analyse and verify that this information exists. Tools such as ChatGPT have been known to create hallucinations and false information as part of citations.
- If using AI to assist your research, use research assistants such as the Primo Research Assistant.
Ask for help:
Still unsure? Can you see that the article exists, but cannot access it? Contact the library.
Librarians can help you verify if the source is real and investigate articles we don't have in our SAE collections via our document delivery service.
